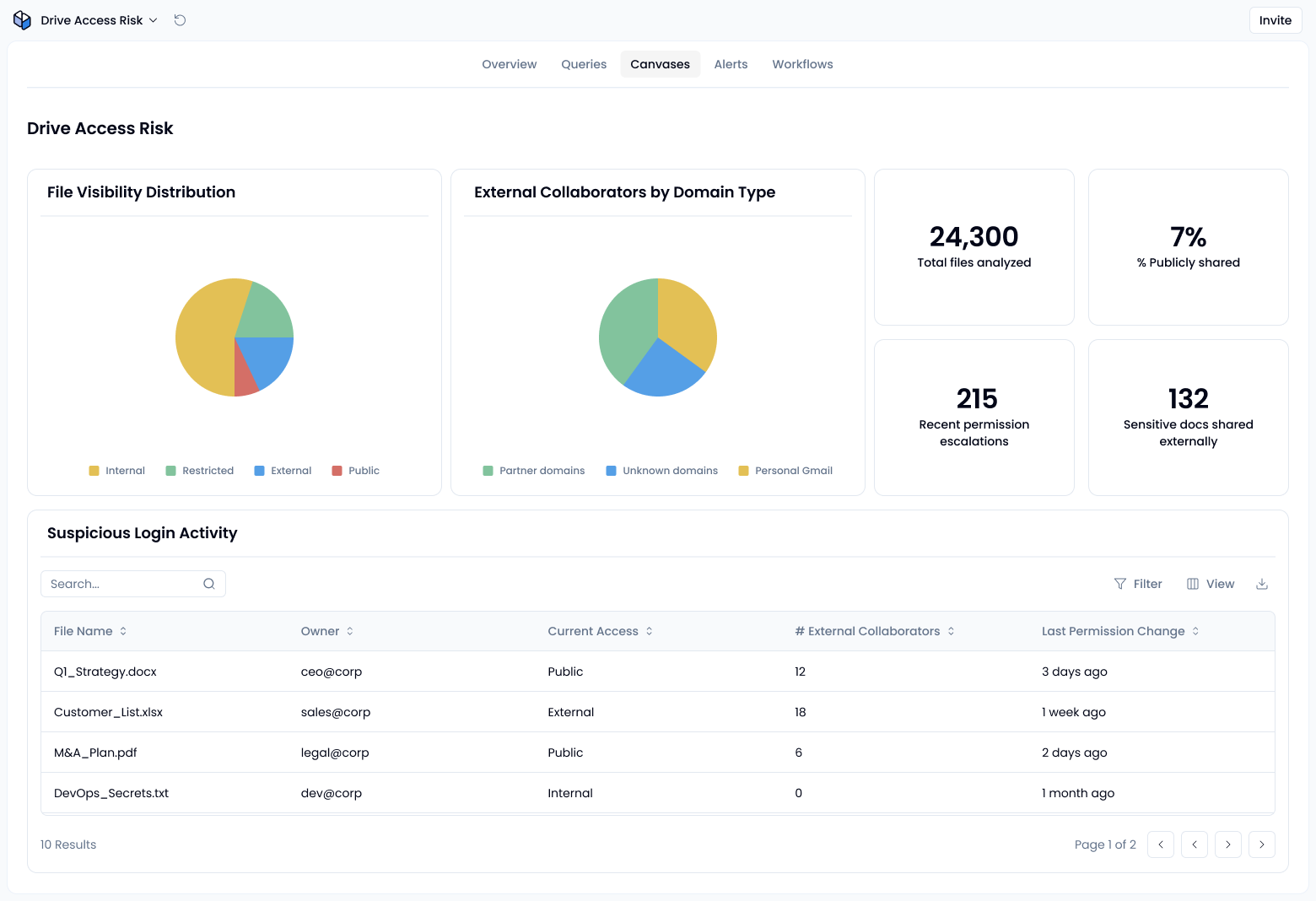
Track public, external, and internal sharing types
With Sola, you can use our AI assistant to analyze Drive permission levels, surface misconfigurations, and monitor access trends across your environment.
Sola apps that could help you
Visit the App GalleryHow to review Google Drive permission levels
1. Inventory permissions by sharing type
Start by listing all Drive files and folders, along with how they’re shared. Group them into:
- Public: Shared with anyone who has the link
- External: Shared with users outside your domain
- Internal: Available to anyone in your organization
- Restricted: Limited to specific users or groups (note: this isn’t a literal Google label, just a useful shorthand for “not shared broadly”)
This classification is essential for understanding Google shared drive permissions at scale.
Sola’s AI assistant can automatically build this view and help you explore each category without manual effort. Without Sola, doing this with Google’s built-in tools usually means running Audit/Investigation reports and CSV exports – not exactly a one-click process.
2. Detect risky sharing behavior
Watch for red flags such as:
- Files shared via public links
- Documents with a high number of external collaborators
- Recent permission changes that expanded access, especially from restricted to public
These are common indicators of weak Google Drive access levels, often caused by unclear file ownership or ad hoc sharing. Sola highlights these patterns using built-in queries so you can focus on the most urgent issues. You can also identify overexposed Drive files by user using AI to flag anomalies quickly.
3. Prioritize based on risk impact
Direct your attention to:
- Sensitive documents shared externally or publicly
- Shared drives with broad access and little oversight
- High-volume users or teams consistently engaging in risky sharing
Sola automatically ranks these based on severity, helping you reduce time spent on investigation and focus on remediation.
Why access control is key to Google Drive security
Without consistent visibility into Google Drive permission levels, it’s easy for sensitive data to slip through the cracks. A single publicly shared folder or overlooked access setting can expose internal content to the wrong audience.
You can also reduce risk up front using Google Admin settings: things like blocking external sharing by default, or warning users when they share outside the domain. The Security Health page in Google Workspace highlights misconfigurations you should fix before they turn into a bigger problem.
Sola lists connected apps by scope, shows who enabled them, and lets you filter for high-risk scopes (like Drive read/write). You can even trigger alerts for newly authorized apps or admin-level grants.
Use AI to stay ahead of permission drift
Sola gives you the tools to monitor Drive access intelligently. Create a custom app to track permissions or let the AI assistant surface public and external sharing risks in seconds. Stay ahead of misconfigurations and reduce exposure across your file ecosystem.
Answer more security questions
How to detect external access in Google Workspace
How to audit file sharing across Google Workspace?
How can I inventory shared Drive files that contain sensitive data?